Cathode Ray Oscilloscope/ Digital Storage Oscilloscope
An oscilloscope is a test instrument which allows us to look at the ‘shape’ of electrical, signals by displaying a graph of voltage against time on its screen. It is like a voltmeter with the valuable extra function of showing how the voltage varies with time. A graticule with a 1cm grid enables us to take measurements of voltage and time from the screen.
Procedure
Switch on the oscilloscope to warm up (it takes a minute or two).
Do not connect the input lead at this stage.
Set the AC/GND/DC switch (by the Y INPUT) to DC.
Set the SWP/X-Y switch to SWP (sweep).
Set Trigger Level to AUTO.
Set Trigger Source to INT (internal, the y input).
Set the Y AMPLIFIER to 5V/cm (a moderate value).
Set the TIMEBASE to 10ms/cm (a moderate speed).
Turn the timebase VARIABLE control to 1 or CAL.
Adjust Y SHIFT (up/down) and X SHIFT (left/right) to give a trace across the middle of the screen, like the picture.
Adjust INTENSITY (brightness) and FOCUS to give a bright, sharp trace.
A calibration point is used to calibrate the CRO.
It gives a steady square wave at a particular set frequency and voltage.
It allows the accurate scaling of the trace. The standard calibration signal is 0V-2V at 1KHz.
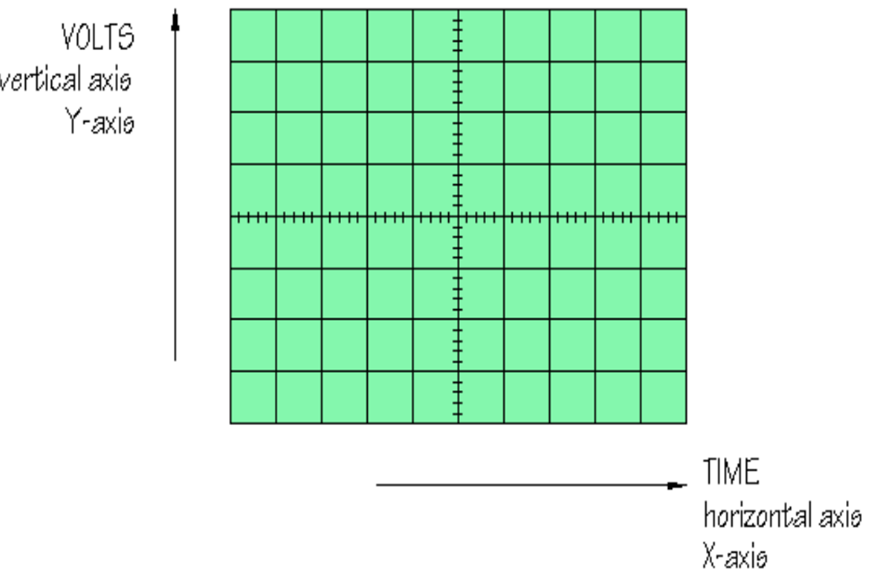
After connecting the oscilloscope to the circuit you wish to test, set the controls to obtain a clear and stable trace on the screen. Most oscilloscopes have a BNC socket for the y input and the lead is connected with a push and twist action.
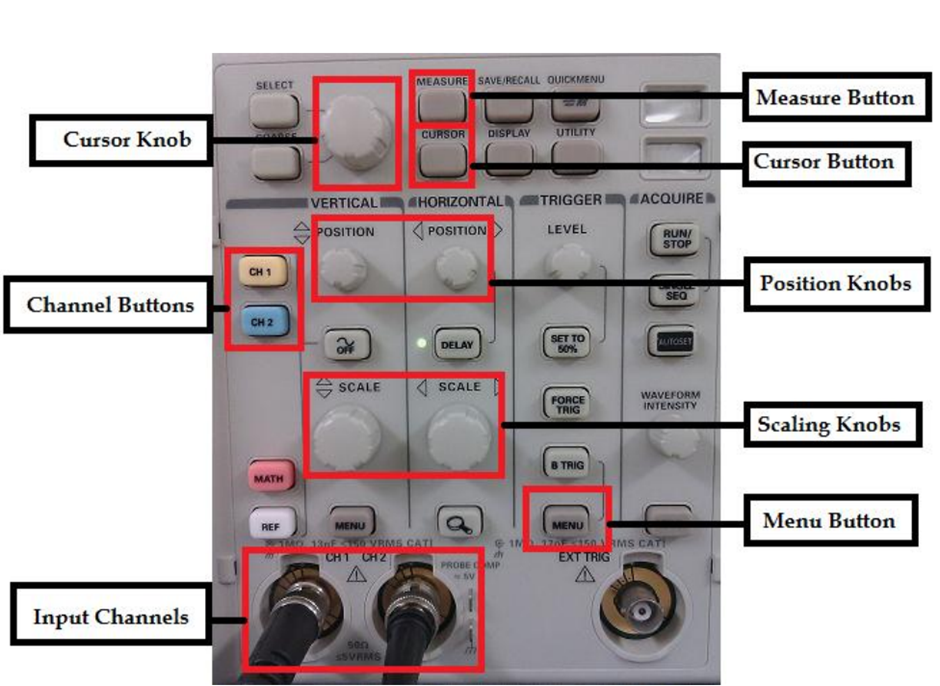
Control Knobs:
The Y AMPLIFIER (VOLTS/CM) control determines the height of the trace. Choose a setting so the trace occupies at least half the screen height, but does not disappear off the screen.
The TIMEBASE (TIME/CM) control determines the rate at which the dot sweeps across the screen. Choose a setting so the trace shows at least one cycle of the signal across the screen. Note that a steady DC input signal gives a horizontal line trace for which the timebase setting is not critical.
The TRIGGER control is usually best left set to AUTO.
AC/GND/DC switch: The normal setting for this switch is DC for all signals – including AC signals! Switching to GND (ground) connects the y input to 0V and allows you to quickly check the position of 0V on the screen. Switching to AC inserts a capacitor in series with the input to block out any DC signal present and pass only AC signals.
Position: Controls horizontal position of trace on screen.
DUAL BUTTON: The oscilloscope has a capability to display both channel signals on the screen at the same time. This is known as DUAL MODE.
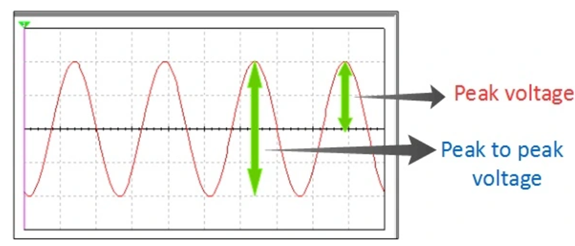
Measurement of peak-to-peak voltage and peak voltage:
To measure the ac. voltage of sinusoidal waveform. The input ac. signal is applied from the signal generator to a channel of CRO. The voltage/div switch (Y-plates) and time base switch (X-plates) are adjusted such that a steady picture of the waveform is obtained on the screen.
The vertical height (L) i.e. peak-to-peak height is measured. When this peak-to-peak height (L) is multiplied by the voltage/div. (voltage deflection sensitivity ‘n’) we get the peak-to-peak voltage (2Vo).
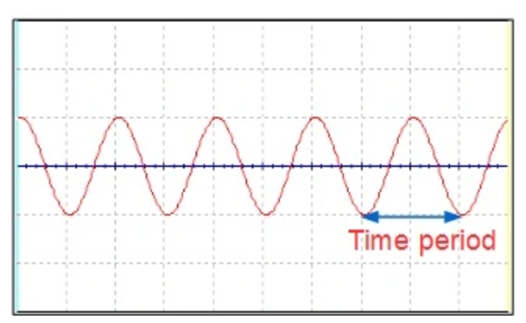
MEASUREMENT OF FREQUENCY
Using time-period: From the trace the time period of the input signal is equal to ‘t’ times the value of time/div setting. Suppose that the time period of the input signal is T. Then, the frequency of the signal =1/T