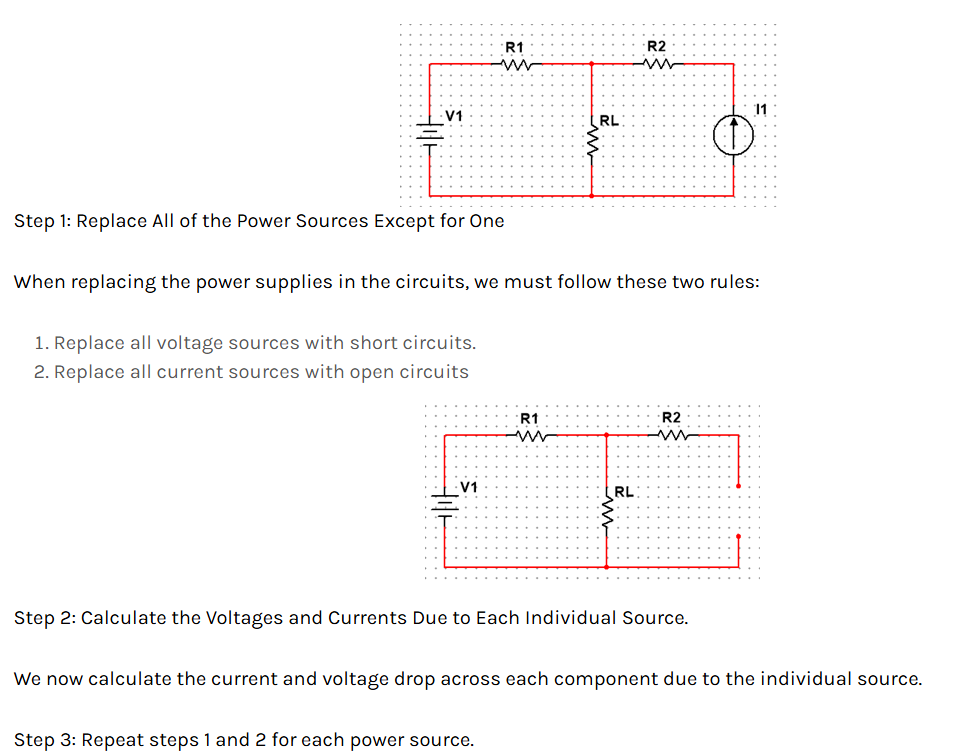
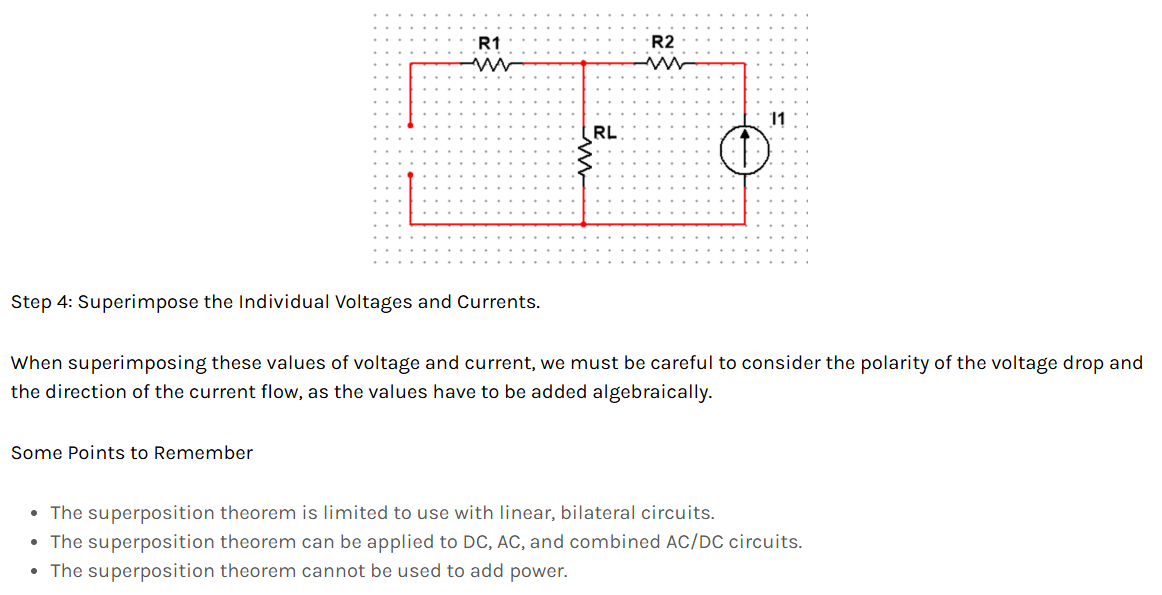
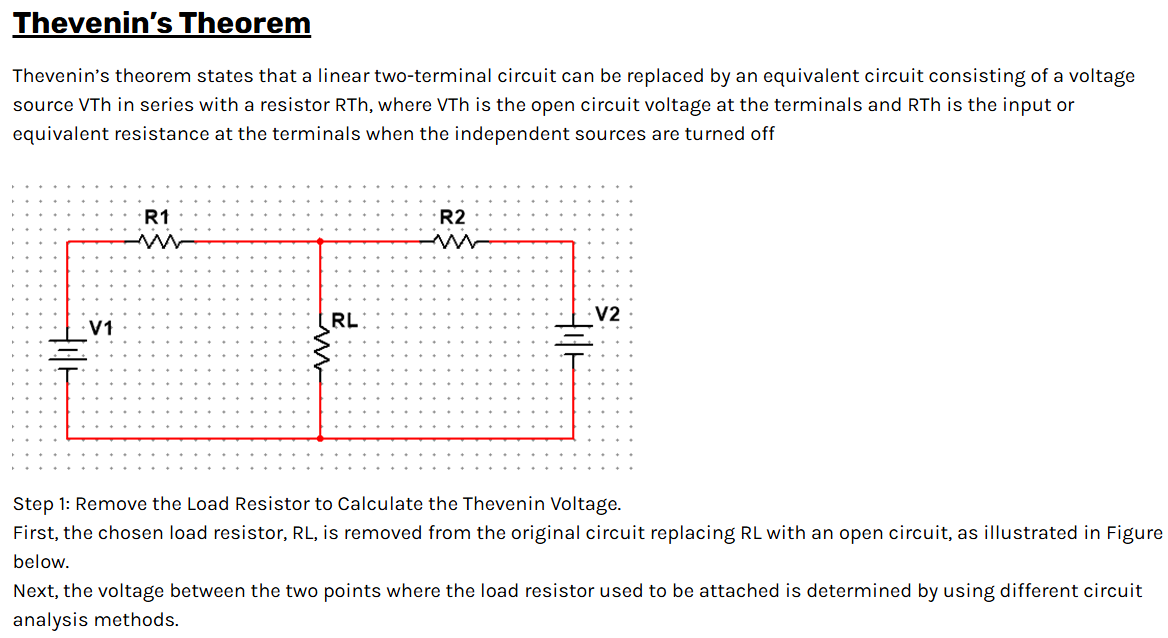
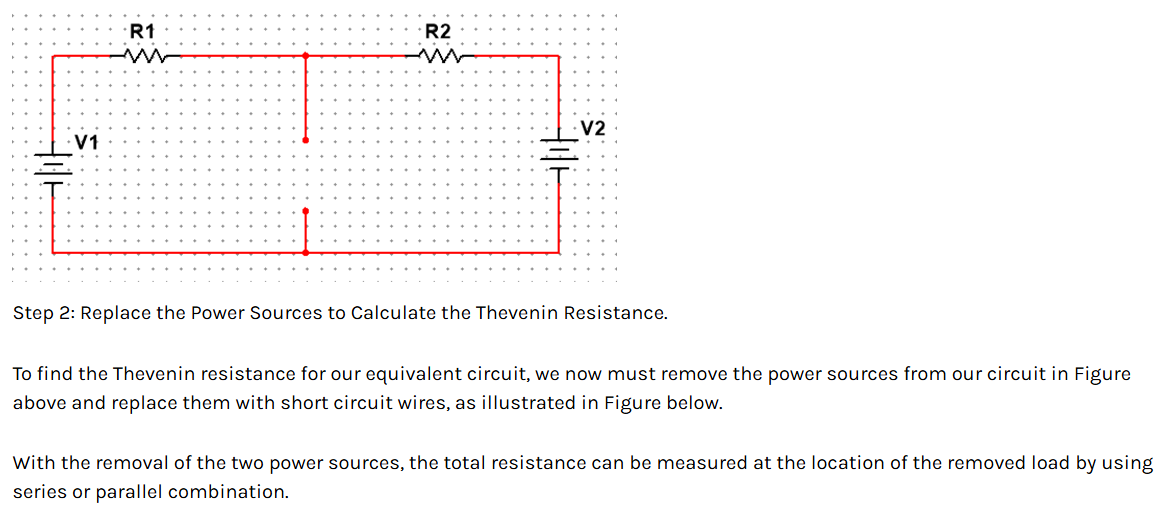
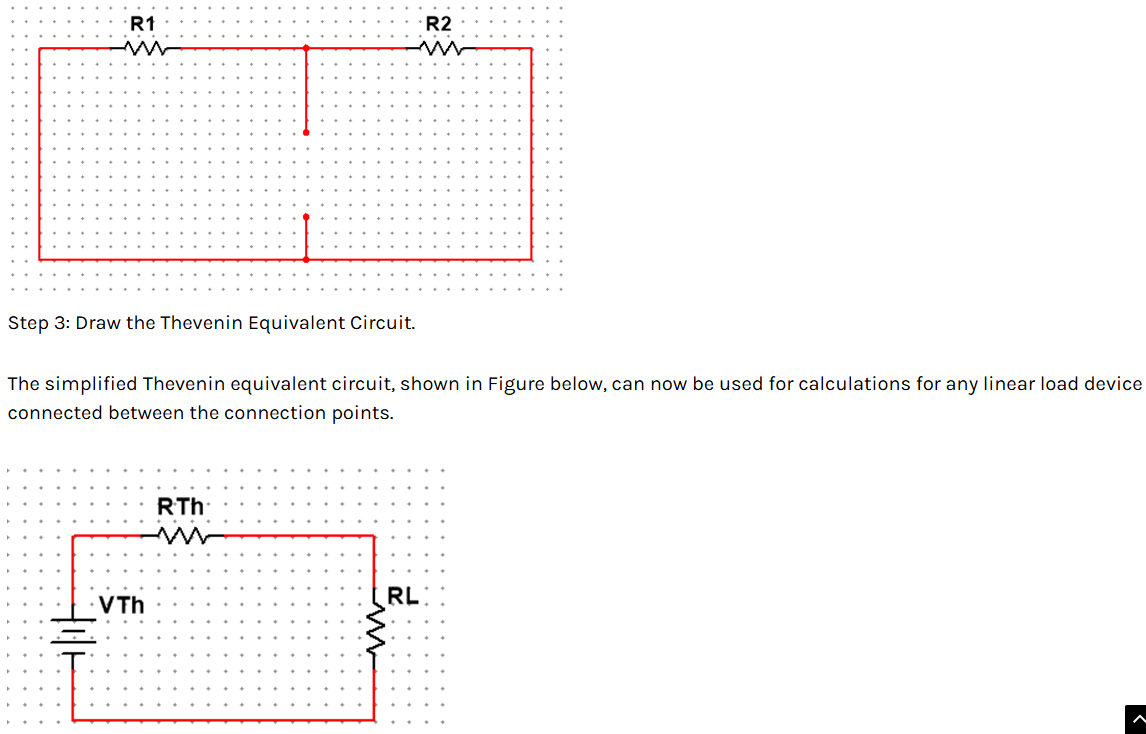
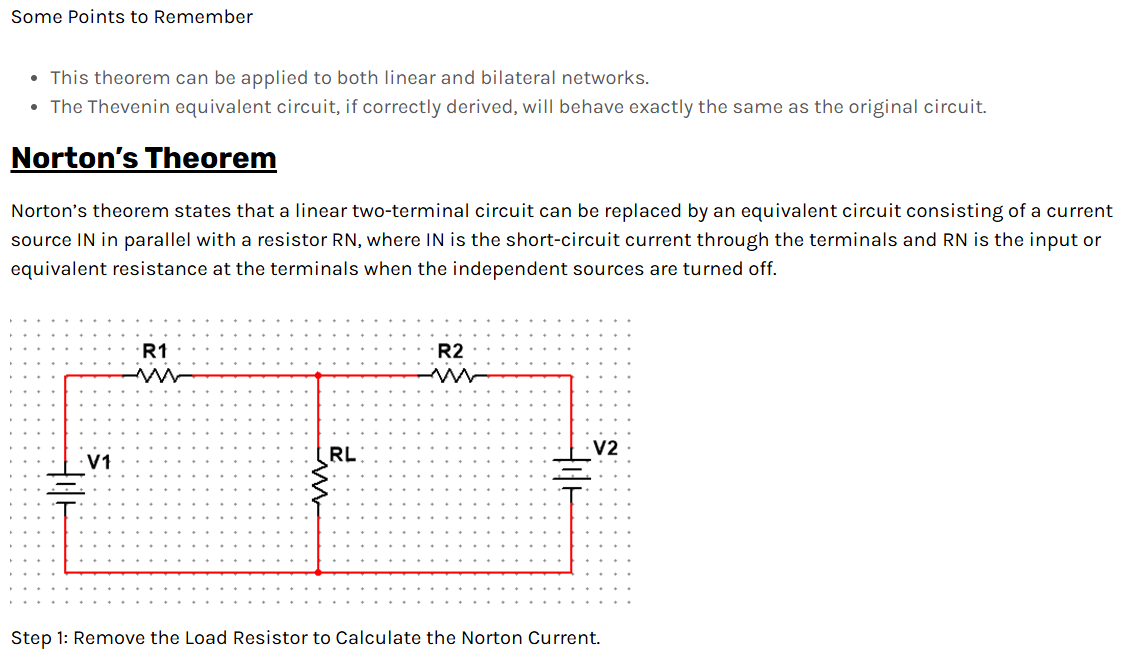
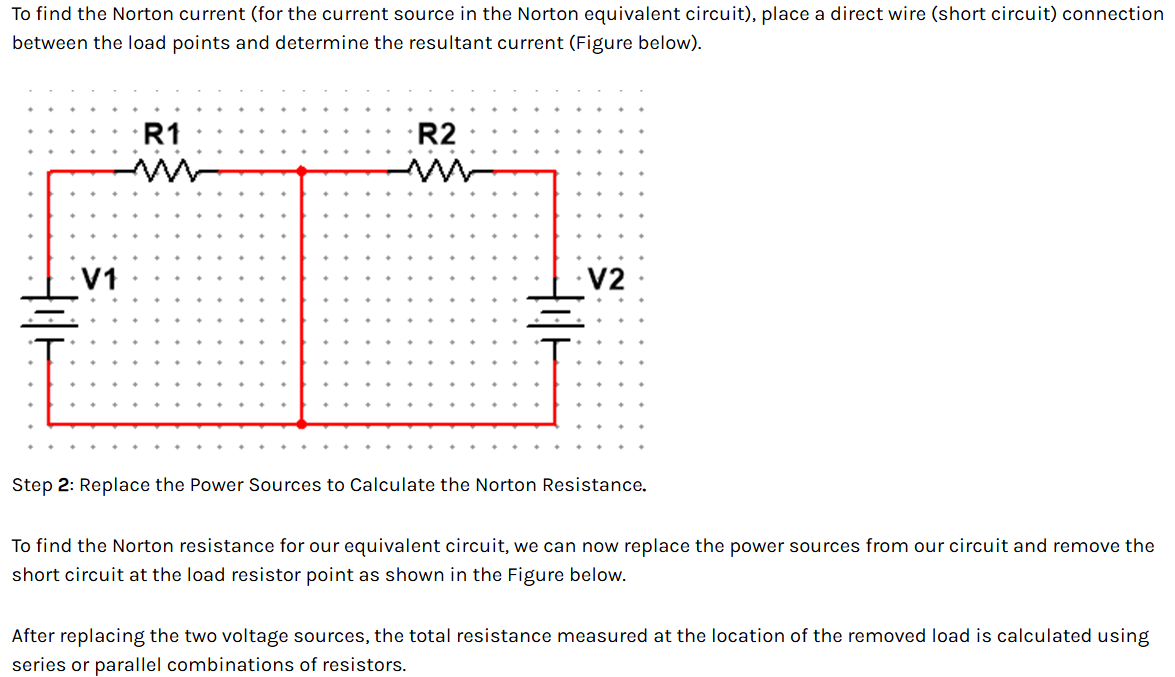
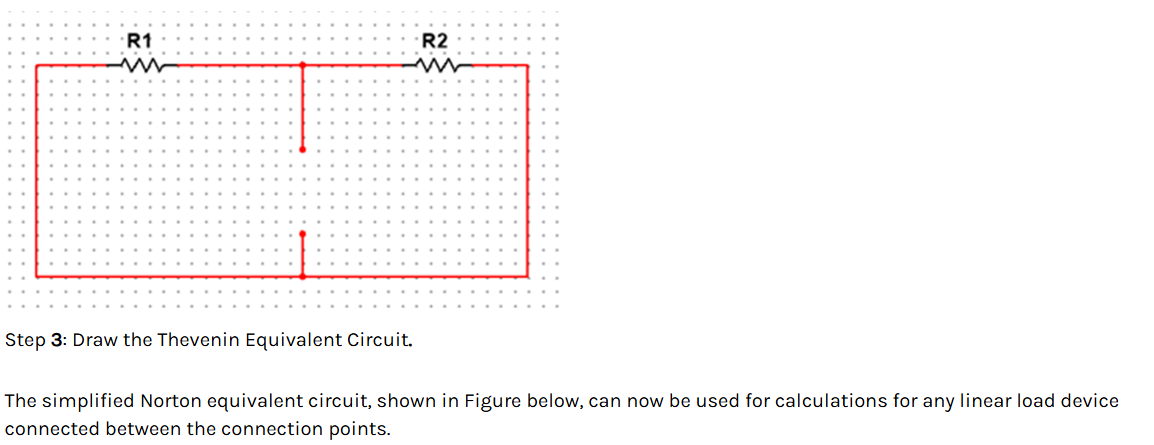
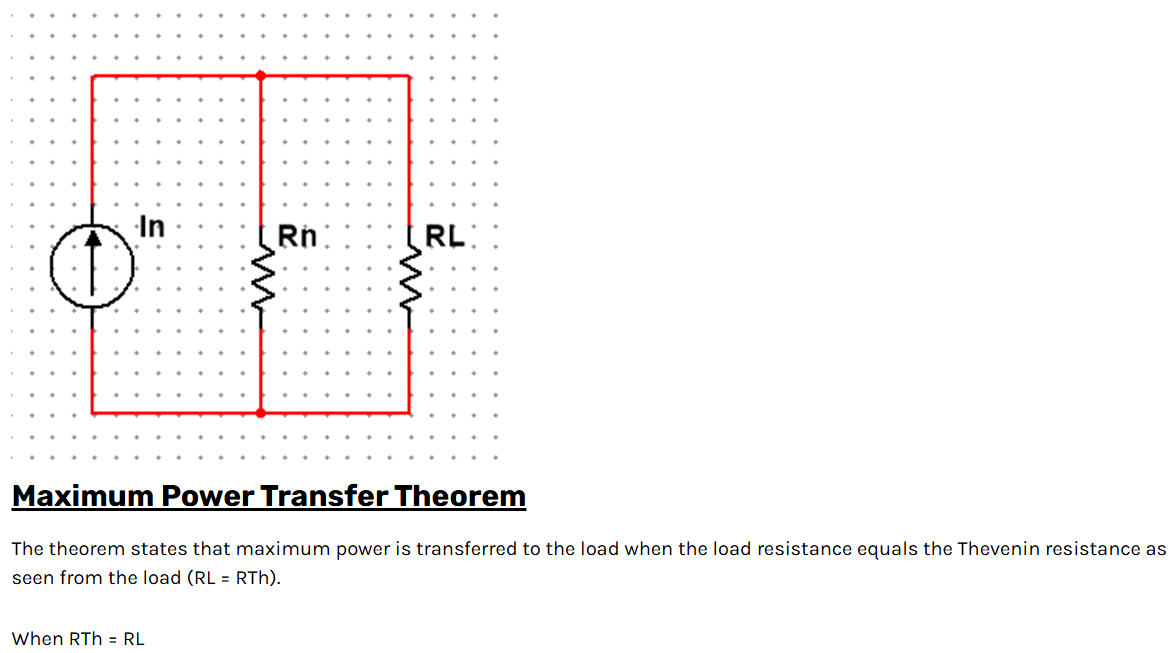
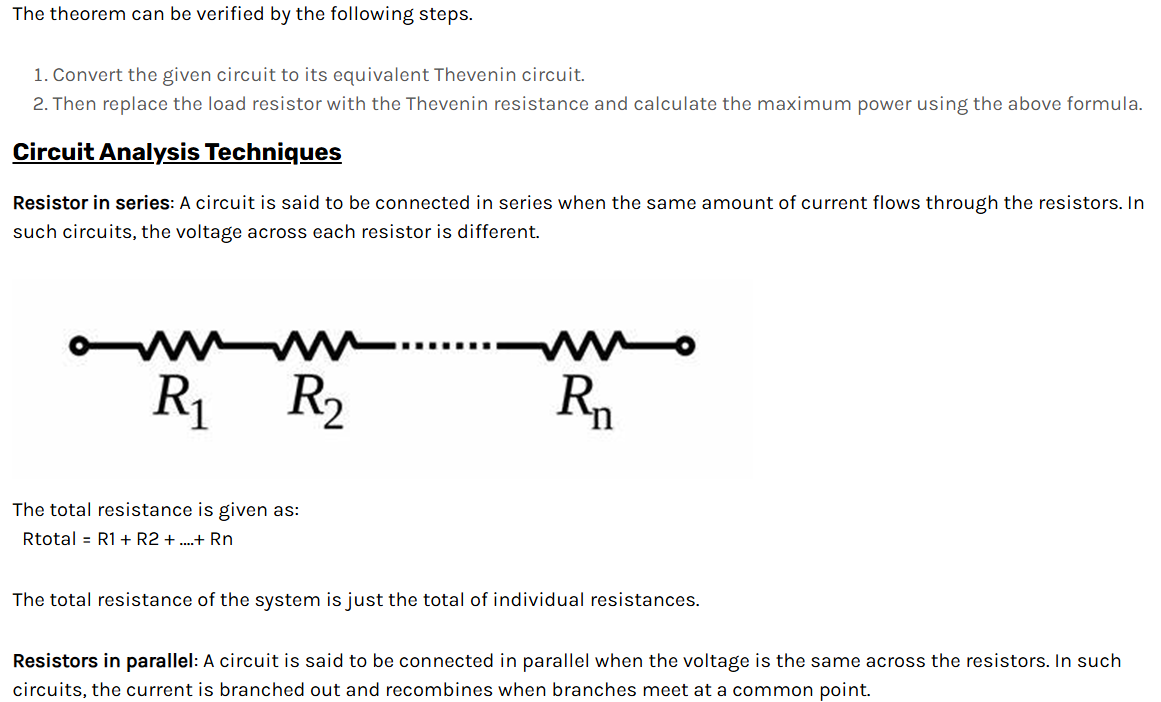
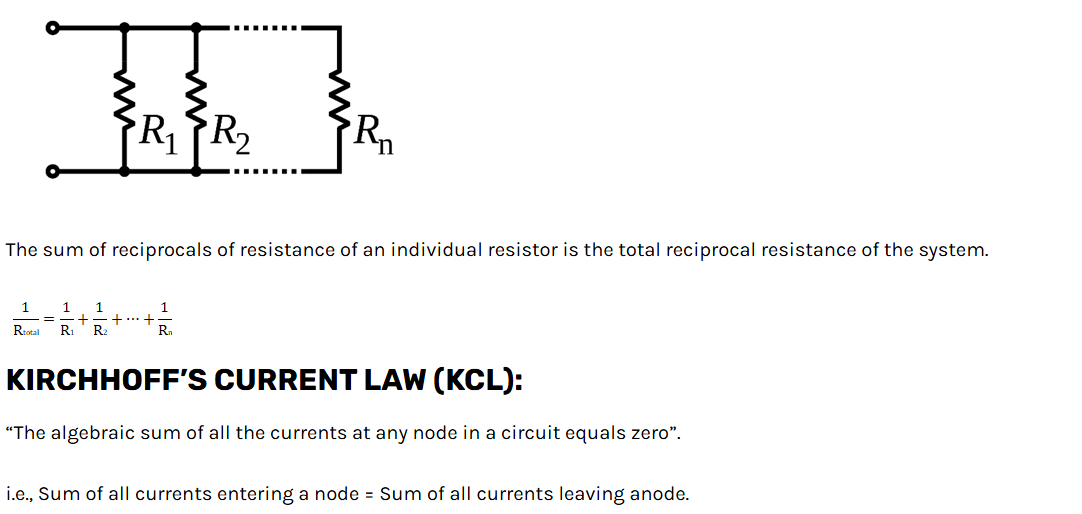
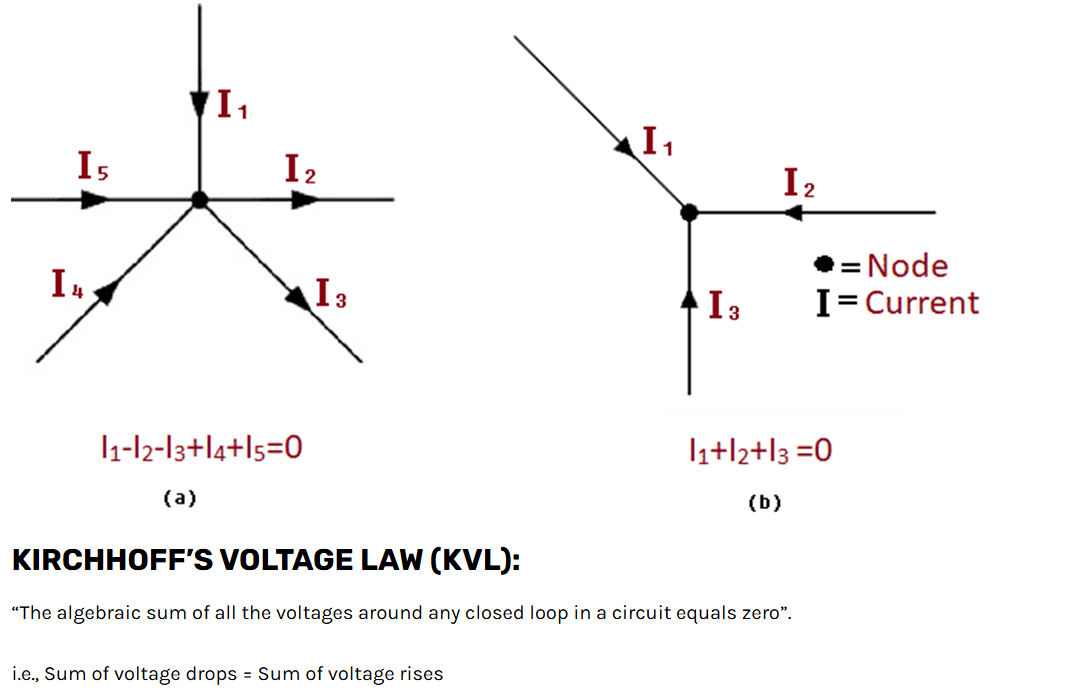
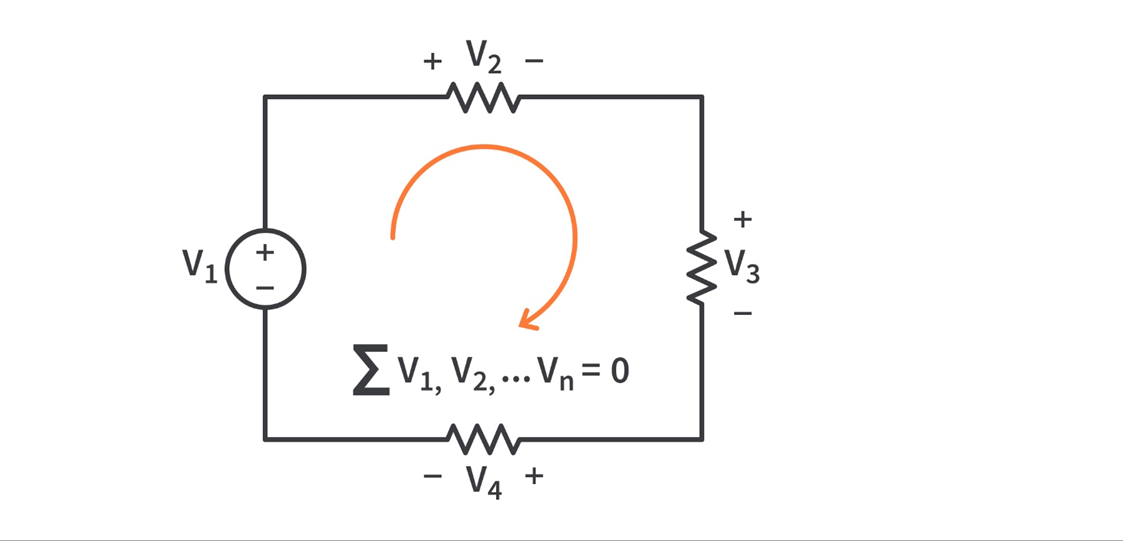
Superposition Theorem
The superposition principle states that the voltage across (or current through) an element in a linear circuit is the algebraic sum of the voltages across (or currents through) that element due to each independent source acting alone. The strategy used in the superposition theorem is to eliminate all the independent sources except one source and find the output voltage/current due to that active source using various circuit analysis techniques.