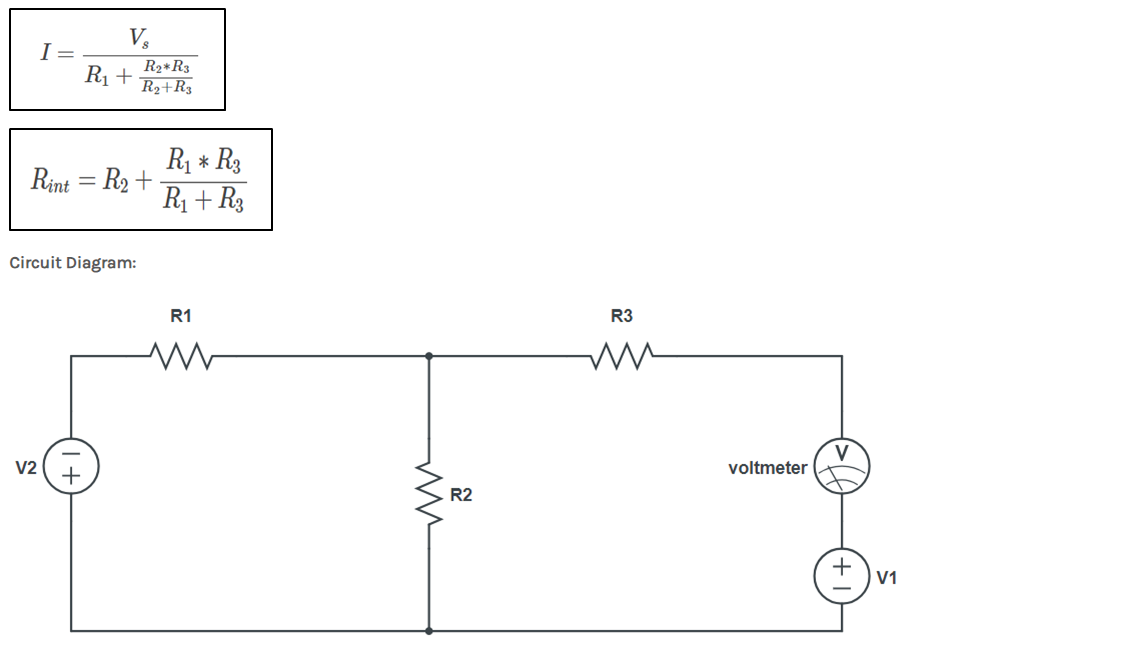
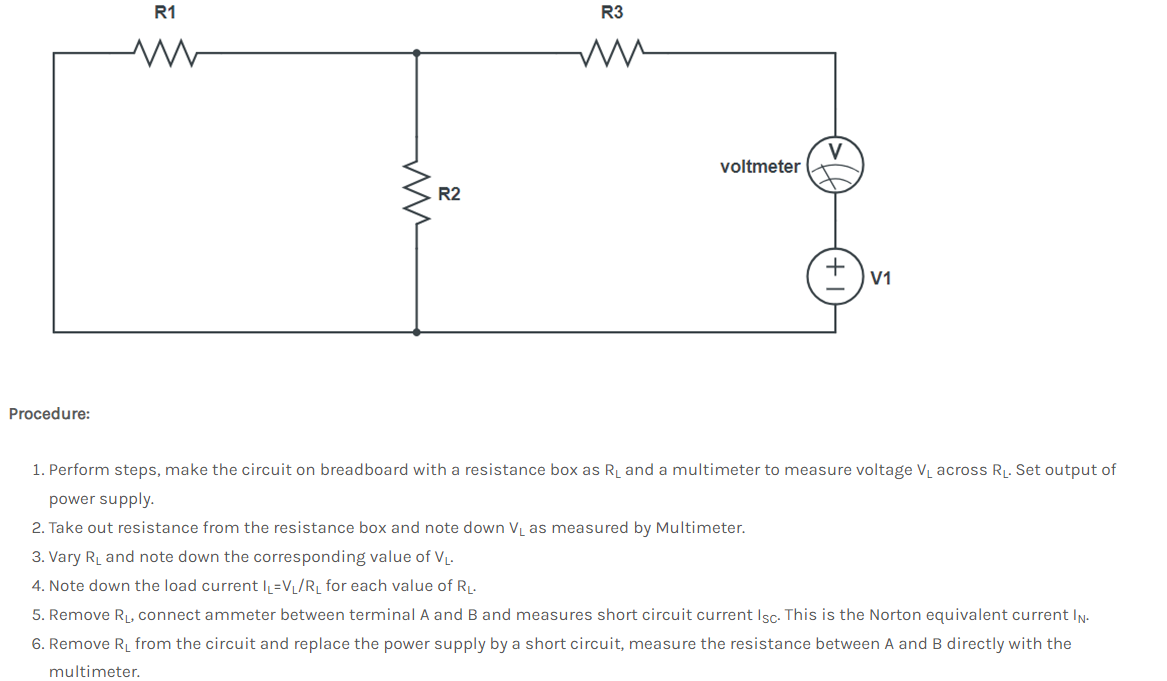
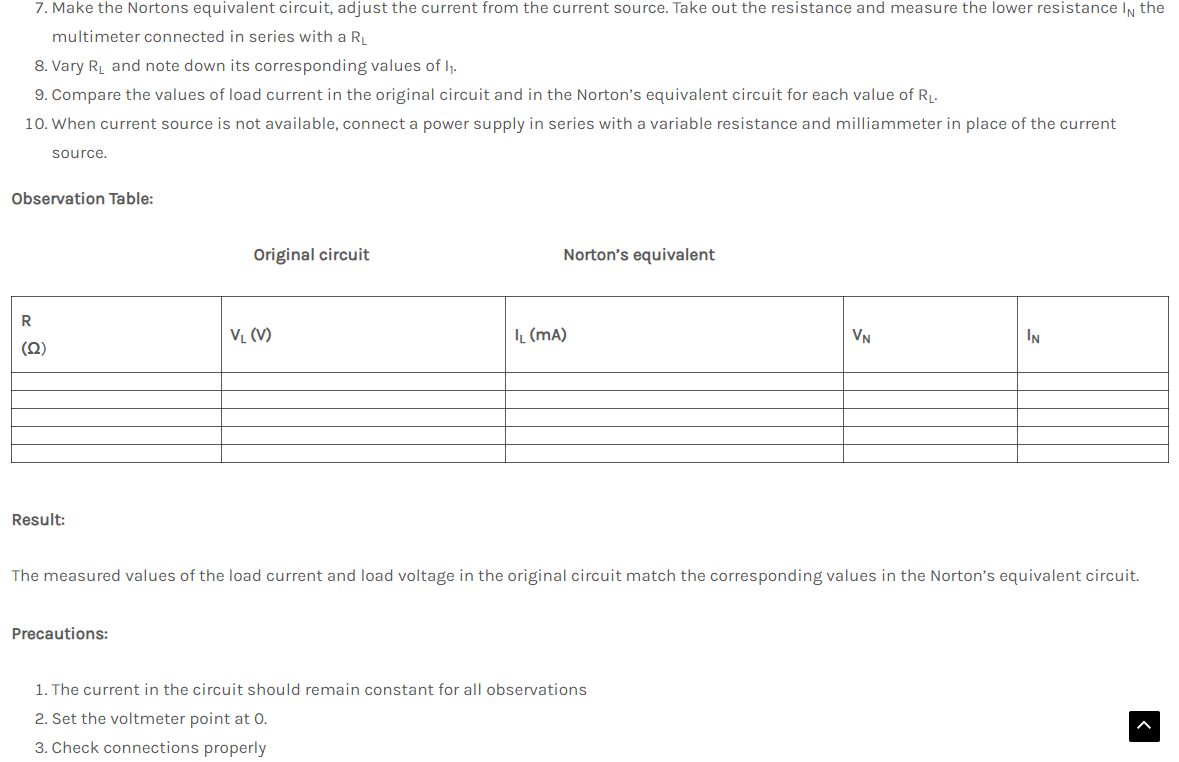
Aim: Verification of Norton’s Theorem
Components and Equipment Required: Variable power supply , 3 resistors, resistance box, constant current source, connecting wires
Theory: Norton’s theorem states that a linear two-terminal circuit can be replaced by an equivalent circuit consisting of a current source IN in parallel with a resistor RN, where IN is the short-circuit current through the terminals and RN is the input or equivalent resistance at the terminals when the independent sources are turned off. The Norton’s equivalent current IN is the short circuit current between the terminals when all voltage sources in network are short-circuited and all current sources are open circuited.